Project Progress
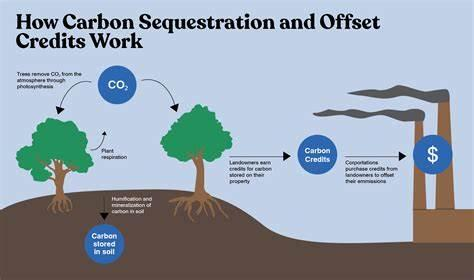
Calculating the Carbon Sequestration of Trees at UR-CST
Author: Desire Bikorimana
Affiliation: Biodiversity Nexus Student Association, UR-CST
Contact Information: [email protected], +250780784924
Introduction/Background
Context:
Urban trees play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere and storing it as carbon in their biomass. The University of Rwanda - College of Science and Technology (UR-CST) is home to a variety of tree species, each contributing differently to carbon sequestration. Understanding the carbon sequestration potential of these trees is essential for the university's sustainability initiatives and Rwanda's broader climate action goals.
Relevance:
Quantifying the carbon sequestration capacity of campus trees provides valuable data that can guide urban planning and conservation efforts at UR-CST. It also helps in assessing the contribution of urban green spaces to Rwanda's national climate goals and informs strategies for enhancing urban forest management.
Problem Statement:
Despite the recognition of the importance of urban trees in climate mitigation, there is currently no comprehensive data on the carbon sequestration potential of trees at UR-CST. This project aims to fill this gap by calculating the carbon storage of different tree species on campus and providing actionable insights for enhancing the university's green infrastructure.
Objectives
Primary Objective:
To quantify the carbon sequestration potential of trees at UR-CST and assess their contribution to climate change mitigation.
Specific Objectives:
- Tree Inventory: Conduct a detailed inventory of tree species on the UR-CST campus, including measurements of tree diameter, height, and age.
- Carbon Sequestration Calculation: Apply standard allometric equations to estimate the above-ground biomass and carbon storage of each tree species.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Analyse the collected data to provide a comprehensive report on the carbon sequestration potential of the campus trees.
- Recommendations: Provide recommendations for enhancing the carbon sequestration capacity of UR-CST’s green spaces through strategic tree planting and management.
Methodology
Tree Inventory:
A systematic inventory of all trees on the UR-CST campus will be conducted. Data collection will include:
- Tree Measurements: Diameter at breast height (DBH), tree height, and crown width.
- Species Identification: Identification of each tree species using botanical keys and local expertise.
- Tree Age Estimation: Using growth rings or species-specific growth rates to estimate tree age.
Carbon Sequestration Calculation:
The carbon sequestration potential of each tree will be calculated using the following steps:
- Biomass Estimation: Applying species-specific allometric equations to estimate the above-ground biomass of each tree.
- Carbon Content Calculation: Assuming that carbon constitutes approximately 50% of the dry biomass, the carbon content of each tree will be calculated.
- Total Carbon Sequestration: Aggregating the carbon content of all trees to estimate the total carbon sequestration for the campus.
Study Design:
The study will be conducted over six months, with data collection occurring in three phases: initial inventory, mid-project review, and final analysis. Sample sites will be selected to represent different areas of the campus, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all tree species.
Expected Outcomes
Climate Mitigation Impact:
The project will provide a clear understanding of the role that UR-CST's trees play in carbon sequestration, highlighting their importance in climate change mitigation. This data can be used to enhance the university's carbon footprint reduction strategies.
Data Generation:
The project will generate valuable data on the biomass and carbon storage of urban trees, which can be used to inform campus sustainability initiatives and urban forestry programs in Kigali.
Capacity Building:
The project will involve training students and staff in tree inventory techniques and carbon sequestration analysis, building local capacity in environmental science and climate change mitigation.
Conclusion
Call to Action:
Understanding the carbon sequestration potential of UR-CST’s trees is a critical step toward enhancing the university's contribution to climate change mitigation. This project will provide the necessary data to inform and support sustainable campus development and urban forestry practices.
Invitation for Support:
We invite you to support this project by providing the necessary funding and resources. Your contribution will help ensure that UR-CST can continue to lead by example in climate action and sustainable urban development.
Status: on hold
Date Posted: March 21, 2025